Performance of a blood-based RNA signature for gemcitabine-based treatment in metastatic pancreatic adenocarcinoma
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC, representing more than 90% of pancreatic cancer cases is a highly lethal cancer, and chemotherapy is a key treatment for advanced PDAC. Gemcitabine chemotherapy is still an important component of treatment. Although, according to several clinical trials (Conroy, T. et al. N Engl J Med. 2011; Von Hoff, D. et al. N Engl J Med. 2013), between 77% and 93% of patients treated by a first-line gemcitabine-based therapy do not respond to their treatment.
But, there is no routine biomarker to predict the efficacy of this chemotherapy. Whereas predictive tests may help clinicians to choose the best first-line treatment.
In collaboration with several French and US clinical partners, ACOBIOM studied the relevance of a blood-based RNA signature, called GemciTest, to predict the patient response to a gemcitabine-based therapy.
This test measures the expression levels of nine genes using real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR) processes. Clinical validation was carried out, through a discovery and a validation phases, on 336 patients (mean 68.7 years; range, 37-88 years) for whom blood was collected from two prospective cohorts and two tumor biobanks. These cohorts included previously untreated advanced PDAC patients who received either a gemcitabine- or fluoropyrimidine-based regimen.
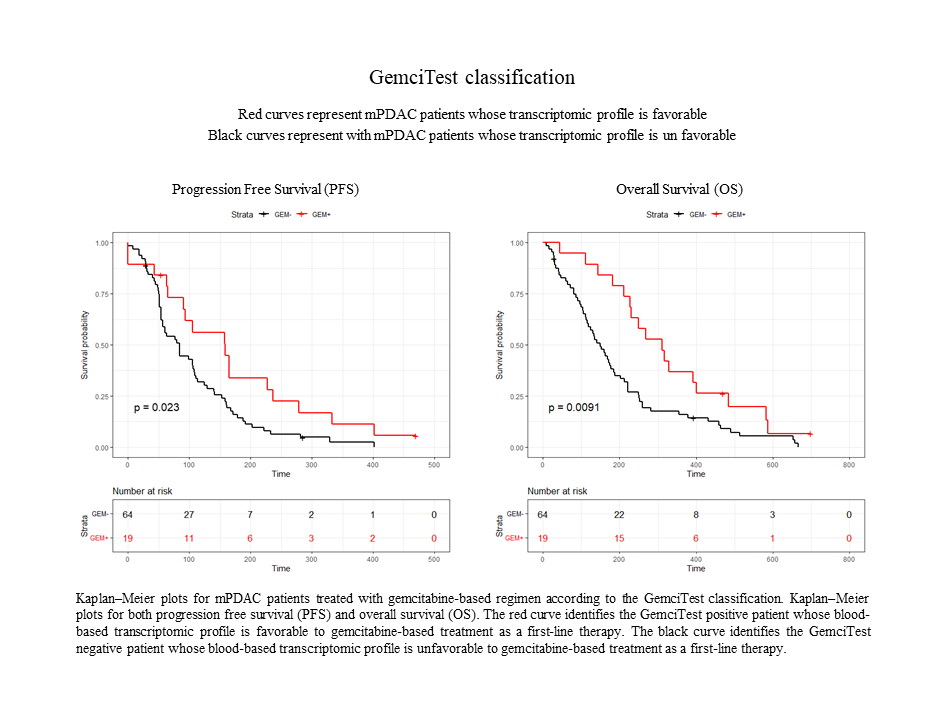
This study confirmed the results obtained in a first discovery phase of RNA biomarkers. Gemcitabine-based treated patients with a positive GemciTest (22.9%) had a significantly longer progression-free survival (PFS) [5.3 vs. 2.8 months] and overall survival (OS) [10.4 vs. 4.8 months]. On the contrary, fluoropyrimidine-based treated patients showed no significant difference in PFS and OS using this blood signature.
In conclusion, the GemciTest demonstrated that a blood-based RNA signature has the potential to contribute to personalized therapy for PDAC, leading to better survival rates for patients receiving a gemcitabine-based first-line treatment.
To obtain more details on these validation study and read the scientific publication associated and published in the Journal of Gastrointestinal Oncology, please click here: JGO 2023 publication.
To obtain more information about the activity of ACOBIOM, please contact the company.

